IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- The use of Paragard is contraindicated when one or more of the
following
conditions exist:
- Pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy, abnormalities of the
uterus
resulting in
distortion of the uterine cavity, acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), postpartum or
postabortal
endometritis in the past 3 months, known or suspected uterine or cervical malignancy,
uterine bleeding of
unknown etiology, untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis or other lower genital tract
infection,
conditions associated with increased susceptibility to pelvic infections, Wilson’s
disease,
a previously
placed IUS that has not been removed, hypersensitivity to any component of Paragard
including to copper or
any of the trace elements present in the copper component of Paragard.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Evaluate for possible ectopic
pregnancy in
any
female who becomes pregnant while using Paragard.
- Intrauterine Pregnancy: Failure to remove
Paragard
increases
the
risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery.
- Sepsis: Severe infection or sepsis, including
Group A Streptococcal Sepsis (GAS), have been reported following insertion of IUSs,
including Paragard.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and Endometritis:
Remove Paragard in cases of recurrent PID or endometritis, or if an acute pelvic infection
is severe or does not respond to treatment.
- Embedment: Partial penetration or embedment of
Paragard in the
myometrium can make removal difficult; surgical removal may be necessary. Breakage of an
embedded Paragard
during non-surgical removal has been reported.
- Perforation: Partial or total perforation of the
uterine wall
or
cervix may reduce contraceptive efficacy and result in pregnancy. Delayed detection or
removal
of Paragard
may
result in migration outside the uterine cavity, adhesions, peritonitis, intestinal
penetration,
intestinal
obstruction, abscesses and/or damage to adjacent organs. Increased risk when the uterus is
fixed,
retroverted
or not completely involuted during the postpartum period. If perforation does occur, locate
and
remove
Paragard promptly.
- Expulsion: Partial or complete expulsion of
Paragard
has been
reported, resulting in the loss of contraceptive protection. The risk of expulsion may be
increased when the
uterus is not completely involuted at the time of insertion. Remove a partially expelled
Paragard.
- Wilson’s Disease: Paragard may exacerbate
Wilson’s
disease.
- Bleeding Pattern Alterations: Paragard can alter
the
bleeding
pattern and result in heavier and longer menstrual cycles with intermenstrual spotting.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety Non-clinical testing has
demonstrated
that Paragard
is MR Conditional.
- Medical Diathermy: Avoid using high
medical RF transmitter devices in females with Paragard.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Adverse reactions reported in clinical trials include anemia,
backache,
dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, expulsion (complete or partial), prolonged menstrual flow,
menstrual
spotting,
pain and cramping, and vaginitis.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
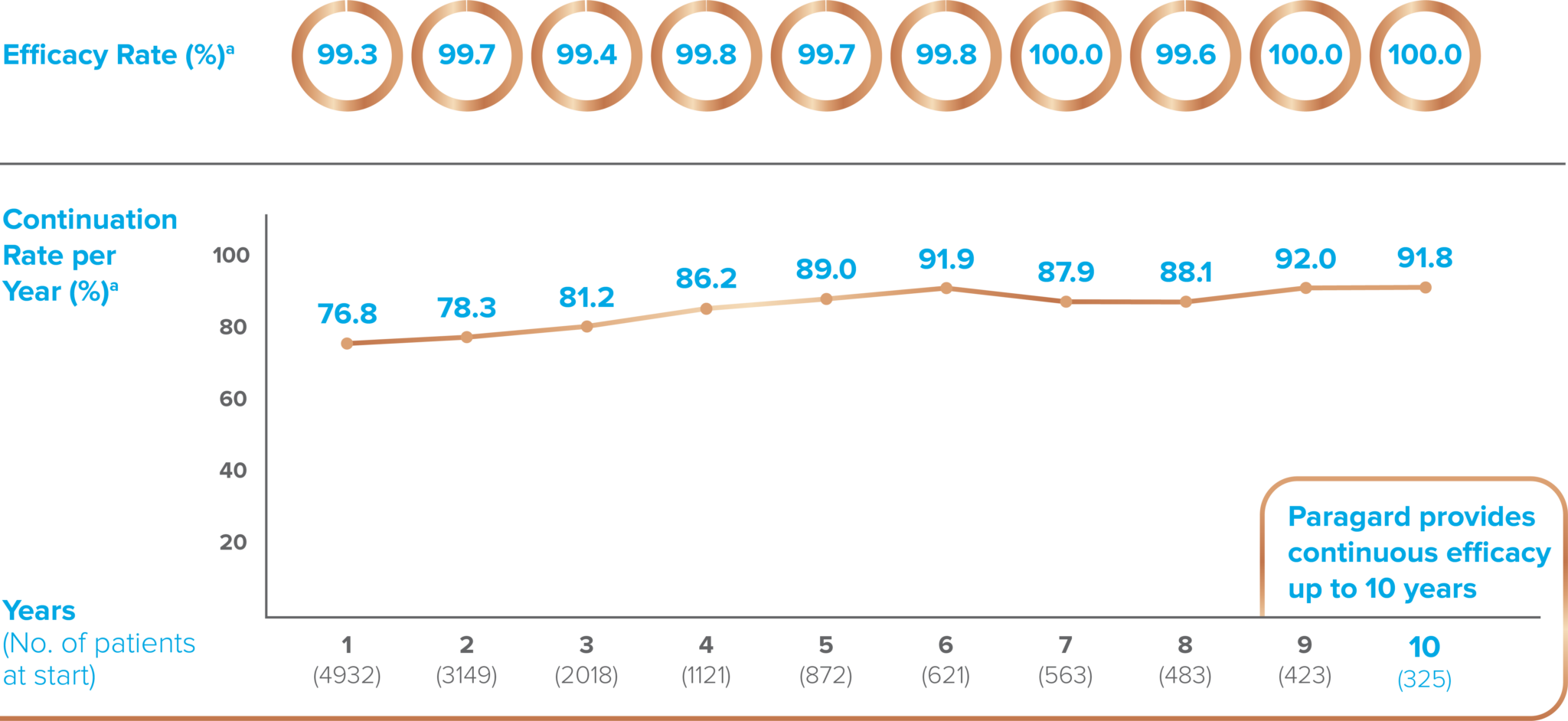
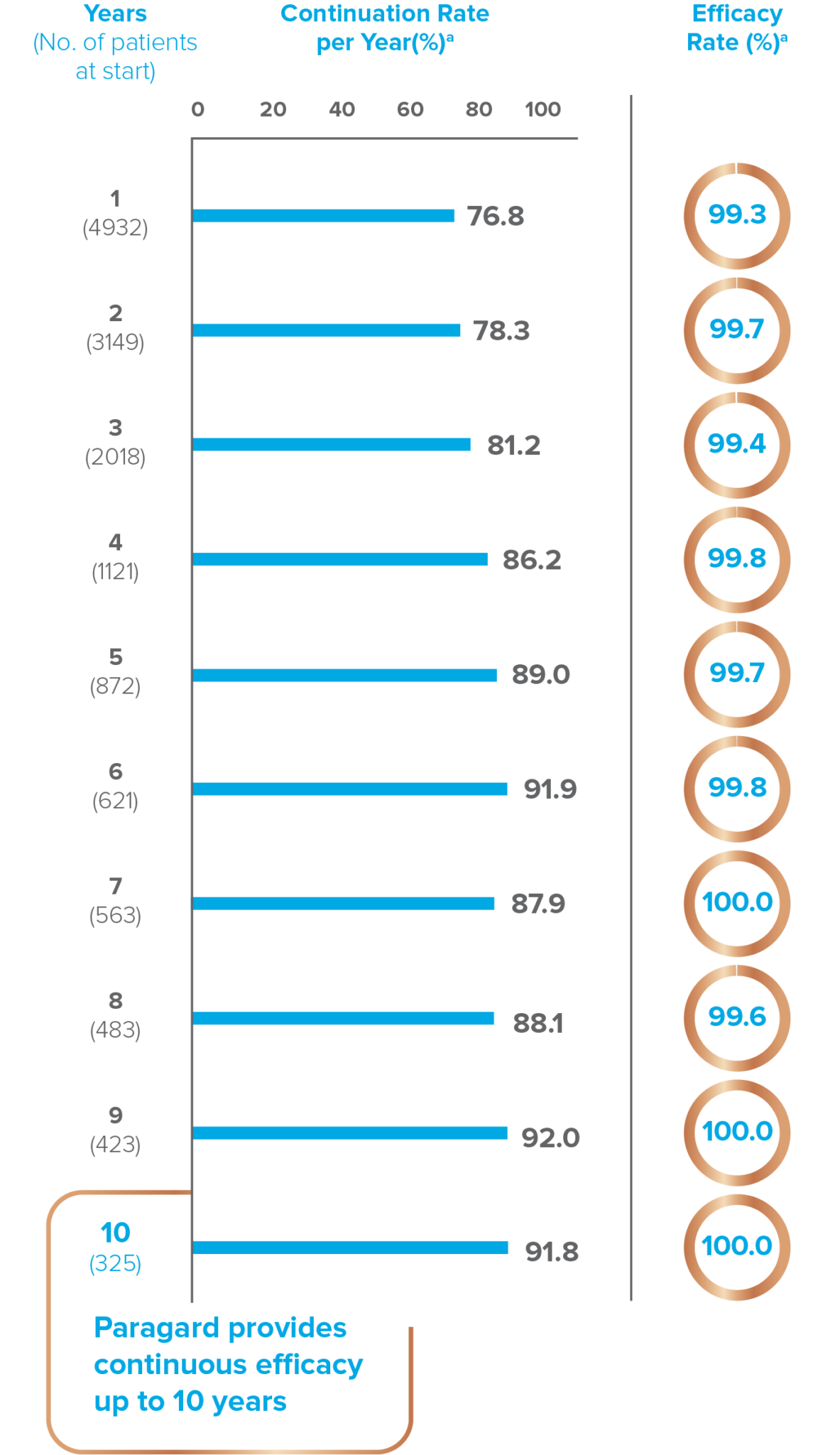
Paragard is a copper-containing intrauterine system (IUS) indicated for prevention of
pregnancy in
females of
reproductive potential for up to 10 years.
References:
1. Paragard® Package Insert, Trumbull, CT: CooperSurgical, Inc. 2024.
2. Trussell J. Contraceptive failure in the United States. Contraception. 2011;83:397-404.
3. Data on File. CooperSurgical, Inc.